宽度优先搜索算法-广度优先搜索
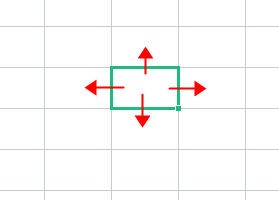
以某点为中心,向四周扩散搜索,直到找到结果为止。
利用该算法搜索迷宫从起点到终点的最优路径.
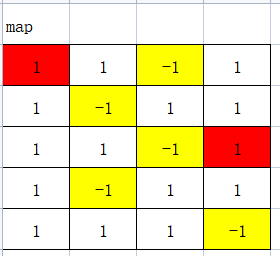
假设有一个上图的迷宫,1表示该点是通路,可以通过,-1表示该点有障碍,不能通过。红色表示迷宫的起点和终点。以上图为例,坐标0:0就是起点,坐标2:3就是终点.
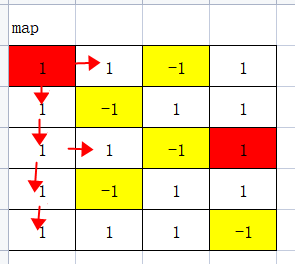
从起点开始,往外扩展,直到找到终点位置.
程序设计:
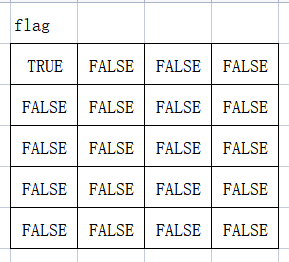
设计flag布尔型数组,用来表示对应的迷宫的格子是否已经访问过,值为false,表示对应的迷宫的格子没有访问过,访问过之后,改为true。
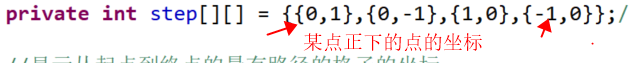
设计step二维数组,分别表示以某点为中心,周围4个点的下标的变化

Cell类表示迷宫的一个格子,x和y表示格子的坐标,stepCount表示到达该格子的步数,pre表示到达该格子之前的格子.

listCell队列,用来保存目前正访问的迷宫的格子.
代码:
cell.java
package com.wanmait;
public class Cell {
private int x;//格子的坐标
private int y;
private int stepCount;//第几步
private Cell pre;//上一个格子
public Cell(int x,int y,int stepCount) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
this.stepCount = stepCount;
}
public void setPre(Cell pre)
{
this.pre = pre;
}
public Cell getPre() {
return this.pre;
}
public int getX() {
return x;
}
public void setX(int x) {
this.x = x;
}
public int getY() {
return y;
}
public void setY(int y) {
this.y = y;
}
public int getStepCount() {
return stepCount;
}
public void setStepCount(int stepCount) {
this.stepCount = stepCount;
}
}Demo.java
package com.wanmait;
import java.util.LinkedList;
public class Demo {
private int map[][];//地图 1 表示可以行走 -1 表示不能走
private int startx,starty,endx,endy;//起点下标 终点下标
private boolean flag[][];//标记对应的点是否走过
private int step[][] = {{0,1},{0,-1},{1,0},{-1,0}};//某个格子周围4个格子的坐标变化的值
//显示从起点到终点的最有路径的格子的坐标
public void showPath(Cell cell) {
System.out.println(cell.getX()+":"+cell.getY());
if(cell.getPre()!=null) {
this.showPath(cell.getPre());
}
}
//x和y起点坐标
public void go(int x,int y)
{
Cell cell = new Cell(x,y,0);//起点
LinkedList<Cell> listCell = new LinkedList<>();//保存经过的格子
listCell.add(cell);//起点保存到队列
flag[x][y] = true;
boolean f = false;//是否到达终点
while(!listCell.isEmpty()) {
Cell first = listCell.getFirst();//取队列的第一个元素
if(first.getX()==endx&&first.getY()==endy)//到达终点
{
System.out.println("步数:"+first.getStepCount());
this.showPath(first);
f = true;
break;
}
//first格子的周围4个格子
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
{
int newx = first.getX()+step[i][0];
int newy = first.getY()+step[i][1];
int stepCount = first.getStepCount()+1;
if(newx<0||newx>4||newy<0||newy>3)
{
continue;
}
if(map[newx][newy]==1&&flag[newx][newy]==false) {
Cell temp = new Cell(newx,newy,stepCount);
temp.setPre(first);
listCell.add(temp);
flag[newx][newy] = true;
}
}
listCell.removeFirst();
}
if(f==false) {
System.out.println("无法到达终点");
}
}
//初始化
public void init()
{
flag = new boolean[5][4];
map = new int[5][4];
map[0] = new int[] {1,1,-1,1};
map[1] = new int[] {1,-1,1,1};
map[2] = new int[] {1,1,-1,1};
map[3] = new int[] {1,-1,1,1};
map[4] = new int[] {1,1,1,-1};
startx = 0;
starty = 0;
endx = 2;
endy = 3;
}
}main
package com.wanmait;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Demo demo = new Demo();
demo.init();
demo.go(0, 0);
}
}









0条评论
点击登录参与评论